Understanding Health Disparities in the US: Healthcare Access and Fitness Culture
Health disparities in the US have long been a significant public health issue. These disparities refer to the differences in health outcomes and access to healthcare across different populations, often influenced by socioeconomic status, race, and geographic location. Addressing these disparities is crucial to ensuring that every individual, regardless of background, has an equal opportunity to live a healthy life.
This blog delves into two major contributors to health disparities: unequal access to healthcare and the fitness culture in the United States. By exploring these two areas, we can better understand how systemic inequality affects overall public health and what can be done to address it.
Healthcare Access Disparities
Healthcare access disparities refer to the unequal availability of medical services across different populations. Despite advances in medical technology and healthcare infrastructure, many Americans still face barriers in obtaining adequate care.
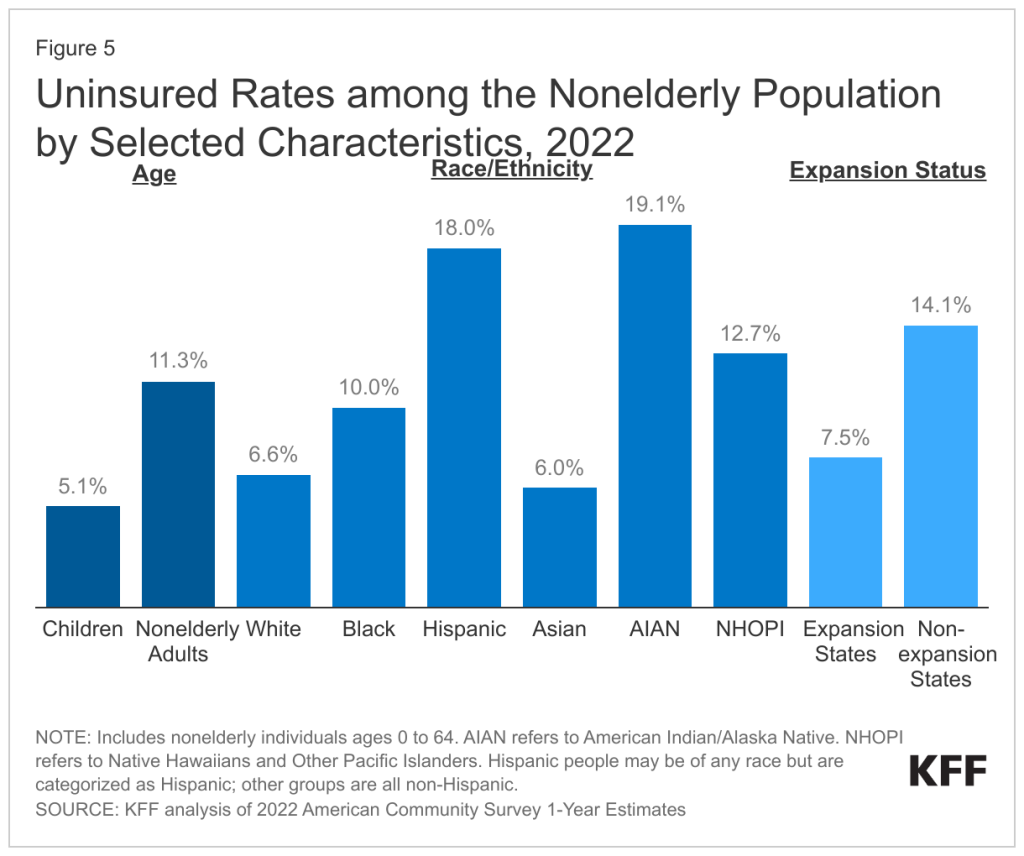
According to a report by the Kaiser Family Foundation (KFF), 9.6% of the US population was uninsured in 2022, with racial minorities and low-income families disproportionately affected.
Furthermore, rural areas face significant challenges due to a lack of healthcare facilities and providers, resulting in inadequate access to basic medical care.
Factors Contributing to Healthcare Disparities
Socioeconomic Status: Income plays a substantial role in determining healthcare access. Low-income individuals often struggle to afford healthcare services, especially those without insurance. They are also more likely to live in areas with fewer healthcare resources.
Insurance Coverage: The uninsured rate for Hispanic individuals was 18%, compared to 6.6% for non-Hispanic Whites, according to the KFF. Medicaid, which serves as a vital resource for low-income populations, varies in coverage across states, creating inconsistent access to services for many Americans.
Geographic Location: Rural and underserved urban communities face a shortage of healthcare providers. Rural hospital closures have compounded the problem, leaving patients to travel long distances for care. In a 2020 study by the National Rural Health Association (NRHA), nearly 70% of rural counties were classified as Health Professional Shortage Areas.
Impact on Health Outcomes
Disparities in healthcare access have a direct effect on health outcomes. Without regular access to preventive care and early intervention, chronic diseases like diabetes, hypertension, and heart disease are more prevalent in underserved communities.
For example, African Americans are 60% more likely to have diabetes than non-Hispanic whites, and lack of adequate healthcare access plays a significant role in this disparity, according to the American Diabetes Association.
Fitness Culture in the US
Fitness has become an integral part of American culture, with gym memberships, boutique fitness studios, and fitness technology booming in popularity. However, participation in fitness activities is far from equal. A study published in the Journal of Physical Activity and Health found that 38% of U.S. adults reported no leisure-time physical activity, while 43% engaged in only one or two activities over the past 30 days.
Socioeconomic and Cultural Factors
- Socioeconomic Status: Wealthier Americans have greater access to fitness facilities and programs. Private gyms, personal trainers, and boutique fitness classes can be prohibitively expensive for lower-income families. In contrast, public recreation centers and community fitness programs are less prevalent in low-income neighborhoods.
- Cultural Perceptions of Fitness: Cultural norms can influence attitudes toward physical activity. Individuals in higher socioeconomic groups view fitness as an essential part of their lifestyle, while those in lower-income brackets may prioritize work and family responsibilities over exercise, viewing it as a luxury rather than a necessity.
Barriers to Fitness Participation
- Access to Facilities: While wealthier urban areas often have an abundance of gyms and parks, fitness resources are scarcer in lower-income neighborhoods. For instance, a report by the Trust for Public Land found that in cities with predominantly low-income residents, only 55% of people live within a 10-minute walk of a park, compared to 88% in wealthier cities.
- Time Constraints: Working-class individuals often have less free time for exercise due to long work hours or multiple jobs, which limits their ability to maintain an active lifestyle. According to a study by Elsevier, high-income individuals report more leisure time for exercise compared to low-income individuals.
- Cost: The average monthly cost of a gym membership in the US is around $58, according to a 2023 IHRSA report. This expense is often out of reach for lower-income families, especially when they have to prioritize basic needs like housing and food.
Addressing Health Disparities: Solutions and Initiatives
Improving Healthcare Access
- Policy Initiatives: The Affordable Care Act (ACA) expanded coverage to millions of previously uninsured Americans, particularly low-income individuals. However, gaps remain, especially in states that did not expand Medicaid. Further expansions and reforms are necessary to provide more equitable access.
- Telehealth Services: The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated the use of telehealth, offering a potential solution for underserved communities. Telehealth allows patients in rural or remote areas to access medical services without having to travel long distances. A report from McKinsey & Company in 2021 showed that telehealth use was 38 times higher than before the pandemic.
- Community Health Centers: Federally funded community health centers (CHCs) are essential in providing care to underserved populations. A study by the National Association of Community Health Centers revealed that CHCs served over 30 million patients in 2020, with 62% being racial or ethnic minorities.
Promoting Inclusive Fitness Culture
- Education and Awareness: Public health campaigns that focus on the benefits of physical activity for all individuals, regardless of income or background, are crucial. Programs like the CDC’s “Active People, Healthy Nation” aim to increase physical activity in communities with lower participation rates.
- Affordable Fitness Options: Community programs that provide free or low-cost fitness opportunities can help bridge the gap. For example, “Parks Rx America” is a program where healthcare providers prescribe outdoor physical activities to patients, encouraging exercise in local parks.
- Role of Schools and Workplaces: Schools and employers can play an active role in promoting physical fitness. Implementing fitness programs in schools and offering workplace wellness programs, including subsidized gym memberships, can have a significant impact on overall physical activity levels.
Healthcare Access Disparities Across States
US States with the Best Healthcare Access
Some states offer significantly better healthcare access due to stronger policies, expanded Medicaid programs, and a higher concentration of healthcare providers.
- Massachusetts: According to a 2023 report by the Commonwealth Fund, Massachusetts ranks first in healthcare access and affordability, largely due to its universal healthcare law that predates the Affordable Care Act. The uninsured rate here is around 3%, one of the lowest in the country.
- Hawaii: Hawaii has a strong healthcare system with one of the lowest uninsured rates (approximately 4%) due to the state’s Prepaid Health Care Act. This mandates that employers provide health insurance to employees working over 20 hours a week.
- Minnesota: Minnesota’s healthcare system benefits from Medicaid expansion and a robust network of community health centers. The uninsured rate here is around 5%, and there is a focus on preventive care, improving health outcomes for low-income populations.
US States with the Worst Healthcare Access
States that have not expanded Medicaid under the Affordable Care Act (ACA) and have fewer healthcare resources face more significant disparities.
- Texas: Texas has the highest uninsured rate in the country, with 18.4% of its population lacking health insurance as of 2023. The state has chosen not to expand Medicaid, leaving many low-income individuals without affordable healthcare options.
- Florida: Florida’s uninsured rate is around 12%, higher than the national average, primarily due to a lack of Medicaid expansion. The state also faces shortages of healthcare providers in rural areas.
- Mississippi: Mississippi tops the list of states with worst healthcare outcomes according to Forbes Advisor. The uninsured rate here is 13.5%, and the state also suffers from a shortage of healthcare professionals in rural areas.
Fitness Culture and Disparities by State
US States with the Most Developed Fitness Culture
States with the best fitness participation rates tend to have more access to parks, recreational facilities, and government programs promoting physical activity.
- Colorado: Colorado ranks as one of the fittest states in the US, with only 24.2% of its population considered obese. Colorado residents are highly active, with access to outdoor activities such as hiking, skiing, and biking being major contributing factors.
- Washington, DC: Washington, DC, also has a strong fitness culture, with a low obesity rate (24.6%) and a high percentage of residents engaging in regular physical activity. Public parks, recreational programs, and fitness facilities are widely available and affordable.
- California: California’s fitness culture is robust, with access to beaches, parks, and fitness centers. Cities like Los Angeles and San Francisco are known for their wellness communities, contributing to lower obesity rates (26%).
States with the Least Developed Fitness Culture
States with high obesity rates and low physical activity often face barriers such as limited access to parks and fitness facilities.
- West Virginia: West Virginia has one of the lowest levels of physical activity, with 28.5% of adults reporting no leisure-time exercise. The state also faces high levels of obesity and limited access to parks and recreational facilities.
- Mississippi: Mississippi has low physical activity rates, with 31.9% of adults not engaging in any form of physical activity outside of work. Limited access to parks and high rates of poverty contribute to a culture where fitness is less prioritized.
- Arkansas: Arkansas has a high obesity rate (37.4%) and low fitness participation. Many residents face barriers such as cost and lack of access to fitness centers or community programs.
Medical Tourism as an Alternative to Address Health Disparities
One alternative to the healthcare access challenges in the U.S. is medical tourism. Medical tourism involves patients traveling to foreign countries for medical procedures, and it has become a popular option for Americans facing barriers to affordable care. With the high cost of healthcare in the U.S., particularly in states like Texas and Florida, where healthcare access is severely limited, many are seeking alternatives abroad.
Why Americans Turn to Medical Tourism
- Cost Savings: Countries like Mexico, India, and Thailand offer medical procedures at a fraction of the cost compared to the U.S. For example, bariatric surgery, and cosmetic procedures can be 50% to 80% cheaper in Mexico compared to the U.S.
- Access to High-Quality Care: Many medical tourism destinations, such as Tijuana, Mexico boast internationally accredited hospitals and highly trained surgeons. These facilities often cater specifically to foreign patients, providing high-quality care and modern amenities.
- Shorter Wait Times: In contrast to long wait times in the U.S., particularly for non-emergency procedures, medical tourists often find that they can schedule surgeries abroad much faster, making it a viable option for those who need timely treatment.
- Wellness Travel: In addition to medical procedures, many people seek wellness-oriented treatments abroad, combining procedures with a holistic focus on recovery. Countries like Mexico also offer post-surgical rehabilitation in serene environments, addressing both physical and mental health in ways that might not be available in U.S. healthcare systems.
How Medical Tourism Helps Combat Disparities
For those in states with the worst healthcare access and highest uninsured rates, such as Texas and Mississippi, medical tourism presents an alternative. It provides an opportunity for patients, particularly those considering bariatric surgery, to get the care they need without being burdened by the exorbitant costs typically associated with U.S. healthcare.
While medical tourism offers a temporary solution to healthcare disparities, it also underscores a deeper issue: that many Americans must go abroad to receive affordable, accessible care. As long as the U.S. healthcare system remains fragmented and expensive, medical tourism will continue to be a growing option for those seeking care outside traditional means.
Conclusion
Health disparities in the US, particularly in terms of healthcare access and fitness culture, remain a persistent issue that requires immediate attention. By addressing systemic inequalities, promoting policies that expand healthcare coverage, and encouraging inclusive fitness opportunities, we can begin to reduce these disparities. A healthier, more equitable society is within reach, but it requires collective action from policymakers, healthcare providers, communities, and individuals.